OSPF as the PE – CE Protocol Notes
OSPF as the PE – CE Protocol
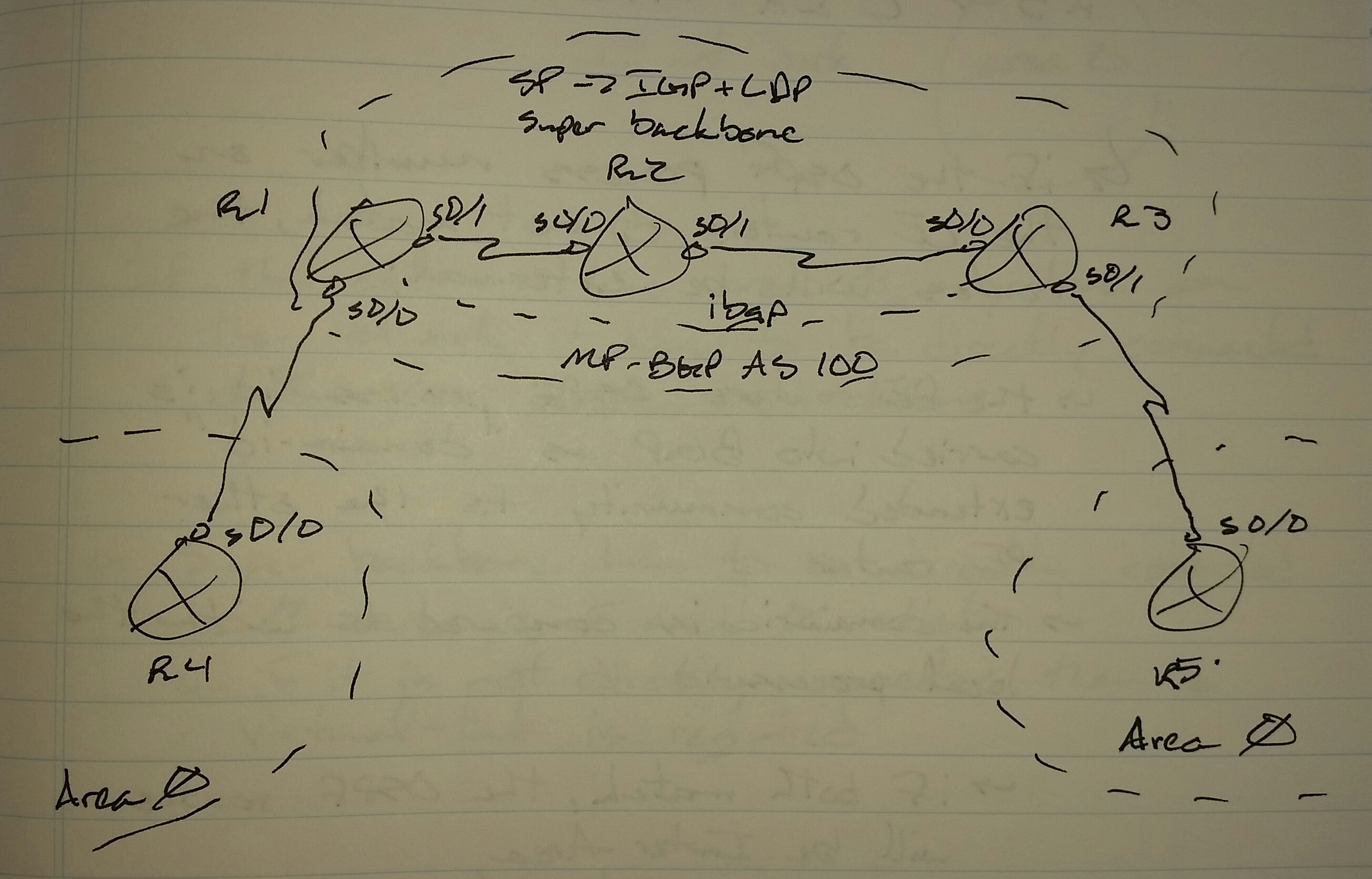
Configuration assumes IGP + LDP is complete, MP-BGP is complete, and CE IGP is complete
R1(config)# router ospf 10 vrf c1b1
network 14.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
redistribute bgp 100 subnets
R3(config)# router ospf 10 vrf c1b2
network 35.0.0.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
redistribute bgp 100 subnets
R1(config)# router bgp 100
address-family ipv4 vrf c1b1
redistribute ospf 100 match internal external 1 external 2
R3(config)# router bgp 100
address-familty ipv4 vrf c1b2
redistribute ospf 10 match internal external 1 external 2
sh ip route
On R4 -> O IA 5.5.5.5
On R5 -> O IA 4.4.4.4
If the OSPF process number on the CE routers do not match, the routes will be external.
– The PE router’s OSPF process-id is carried into BGP as the “domain-id” extended community to the other PE router
– The domain-id is compared with the local process-id
-> If they match, the OSPF routes will be Inter-Area
-> If the do not match, the OSPF routes will be external (E2)
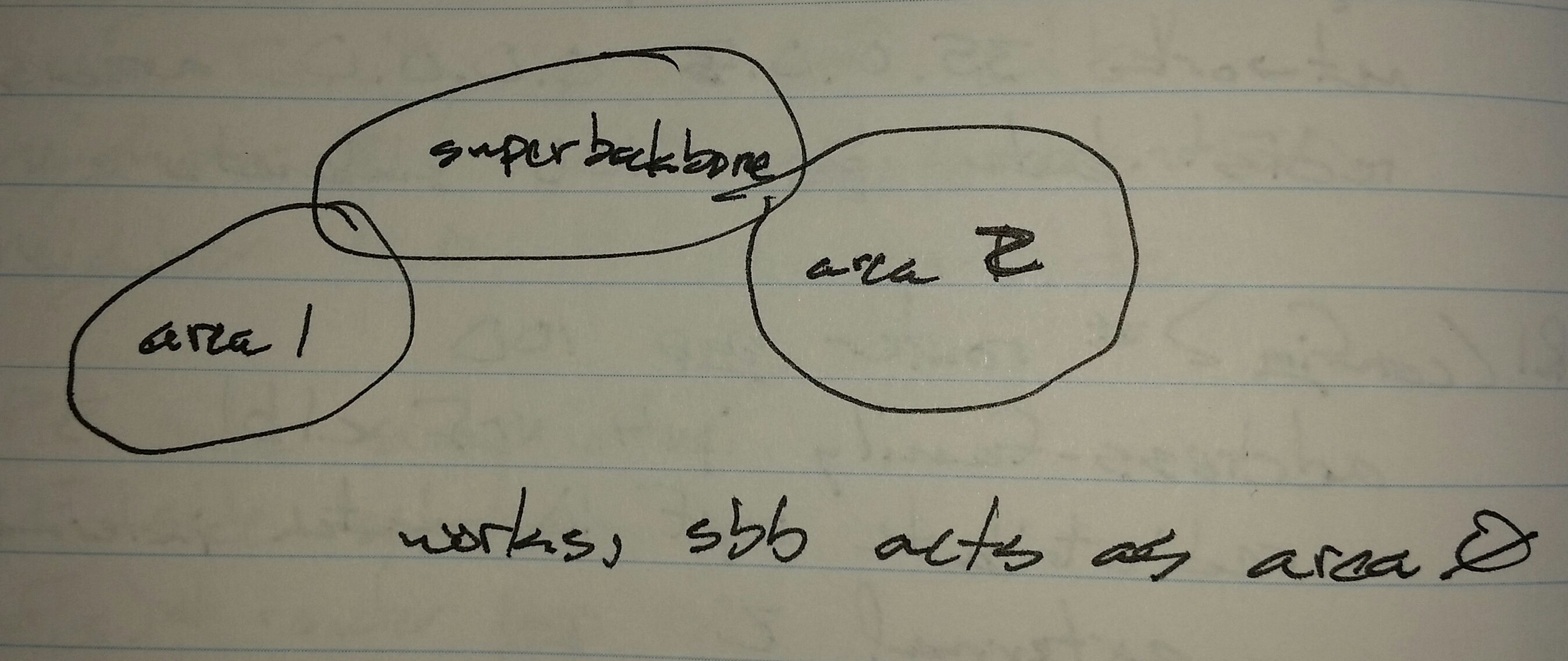
The PE network acts as a super backbone area for the customer’s OSPF.
Instructor comment, “The super backbone is like a higher, more intellignt area 0.”
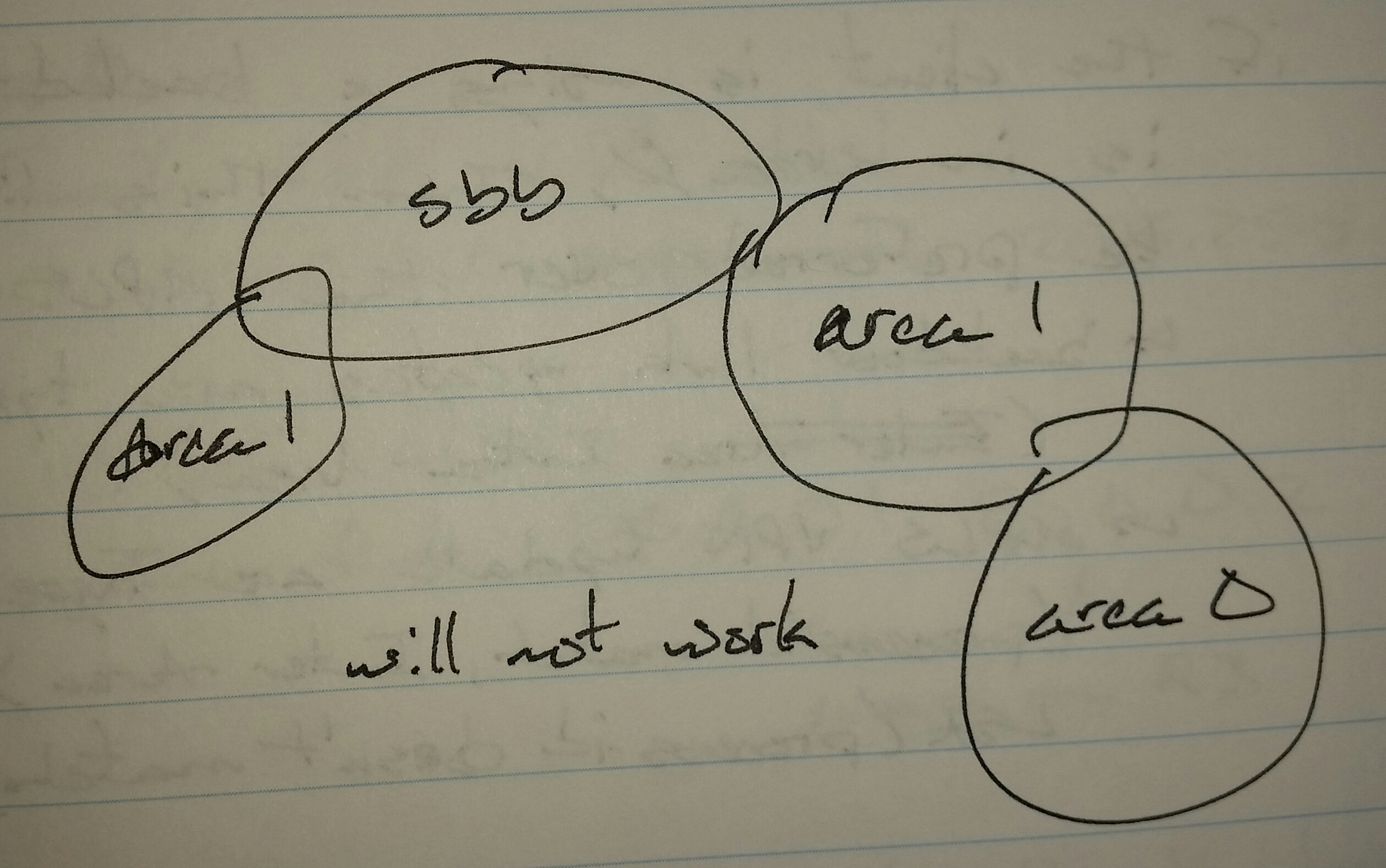
If the customer has area 0 anywhere on the network, it has to be directly connected with the super backbone
-> If area 0 is not directly connected with the super backbone, virtual-links are required

