RIPv2 Notes
RIPv2:
– UDP port 520
– Multicast IP 224.0.0.9
– Classless (not by default)
-> Cannot have discontiguous networks
– Metric is hop count
– Metric 16 is infinite metric
– Timers
-> Update timer: 30 seconds
-> Invalid timer: 180 seconds
-> Holddown timer: 180 seconds
-> Flush timer: 240 seconds
– Supports authentication
-> Plain text
-> MD5
– AD is 120
router rip
version 2
no auto-summary
network x.x.x.x
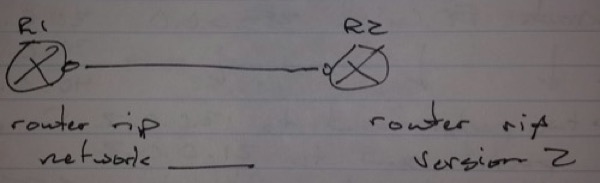
Mismatched version updates can cause one way communication between the routers
– R1
-> Send v1 updates
-> Receive v1 and v2 updates
– R2
-> Send and receive v2 updates
Authentication
– Plain text
– MD5
-> Create key chain
-> Apply to an interface
key chain CISCO
key 1
key-string CCIE
int s0/0
ip rip authentication mode { text | md5 }
ip rip authentication key-chain CISCO
sh ip protocols
– Lists the authentication method
debug ip rip
– To troubleshoot authentication problems
-> Such as key mismatch
sh key chain
– To see if a space is present in the key-string
Summarization
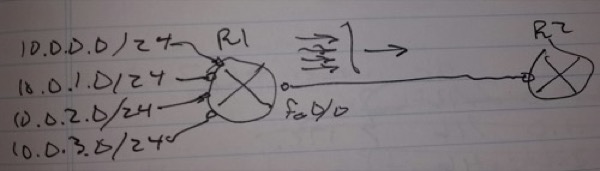
Summary address 10.0.0.0/22
int fa0/0
ip rip summary-address 10.0.0.0 255.255.252.0
A summary address is installed into the routing table pointing to the NULL interface
– Used when one of the more specific networks is not rachable
– This prevents the packets from being default routed to 0.0.0.0/0
– Causes packets to be dropped
– Summary address AS is still 120
RIP does not create a summary route pointing to NULL0
– Must be created manually
ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.252.0 NULL0
172.16.0.0 /24
172.16.1.0 /24
172.16.2.0 /24
172.16.3.0 /24
-> 172.16.0.0 /22
-> Works with RIPv2
172.0.0.0 /16
172.1.0.0 /16
172.2.0.0 /16
172.3.0.0 /16
-> 172.0.0.0 /14
-> Will not work with RIPv2
-> Error message when trying to configure
RIPv2 summarization is only possible within the limits of a class (A, B, C)
-> RIPv2 summarization is not classles
Default Routing
R1(config)# router rip
default-information originate
In other routing tables:
R* 0.0.0.0 [120|*]
-> The metric of the summary route is the least metric among more specific routes
Conditional Default Routing
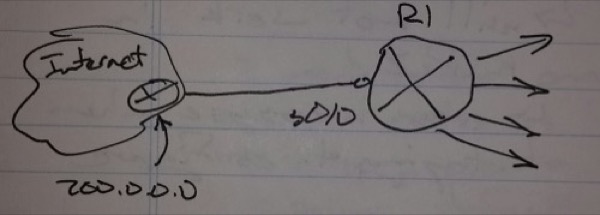
In conditional default routing, the exit interface network is checked
– If the network is in the routing table, the default network will be injected
– If the network is not in the routing table, the default route is not injected
R1(config)# access-list 1 permit 200.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
route-map DR
match ip address 1
router rip
default-information originate route-map DR
This is conditional, but not reliable
– Have to make the route-map false to be reliable
– Link may be up, but the connection to the Internet may be down
Reliable Conditional Default Routing
– Uses IP SLA
Apply to RIP
– IP SLA (Step 1) <–> Track (Step 2) <– Dummy Static Route (Step 3) <– Access-list (Step 4) <– Route-map (Step 5)
R1(config)# ip sla 1
icmp-echo 4.2.2.2
timeout 2000
-> In milliseconds
frequency 4
-> In seconds
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
ip route 169.254.0.0 255.255.0.0 NULL0 track 1
access-list 1 permit 169.254.0.0 0.0.255.255
route-map ABC
match ip address 1
router rip
default-information originate route-map ABC
RIP Filtering
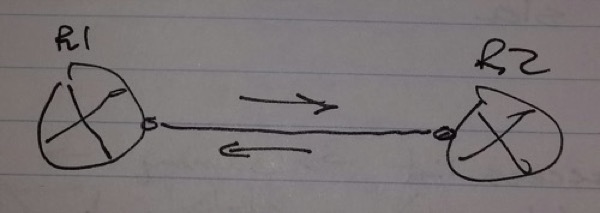
Passive Interface
– It stops sending updates out the specified interface
router rip
passive-interface { <interface> | default }
passive-interface default
– Can be used if there are a lot of loopback interfaces that you do not want to advertise
Distribute List
– Which network to filter
– Direction ( in | out )
– In | out which interface
-> If not specified, the network will be filtered from all interfaces
– Filter is outsourced!
-> ACL
-> Prefix-list
router rip
distribute-list <acl> in | out int <int>
router rip
distribute-list prefix <list> in | out int <int>
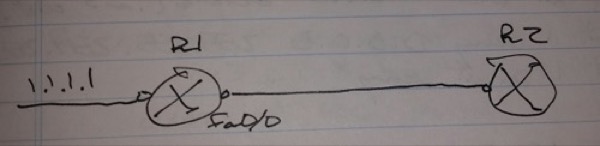
Distribute List – Standard ACL
access-list 1 deny 1.1.1.1
access-list 1 permit any
router rip
distribute-list 1 out fa0/0
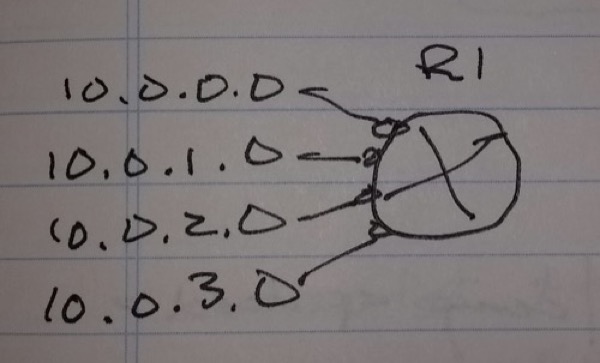
Scenario -> Filter all even number octets (in the 3rd octet) of outgoing network
255.255.11111110.255
-> I don’t care about the first 7 bits, I only care about the last bit
-> Subnet mask: 255.255.254.255
-> Wild card mask: 0.0.1.0
10.0.0.0 – 00000000
10.0.2.0 – 00000010
-> Last bit doesn’t change
-> 0 – don’t care
-> 1 – do care
access-list 1 deny 0.0.0.0 255.255.254.255
access-list 1 permit any
– or –
access-list 1 permit 0.0.1.0 255.255.254.255
Distribute List – Extended ACL
access-list <number> permit | deny <protocol> <source> <destination>
– Protocol is ip
– Source is update source
– Destination is update network
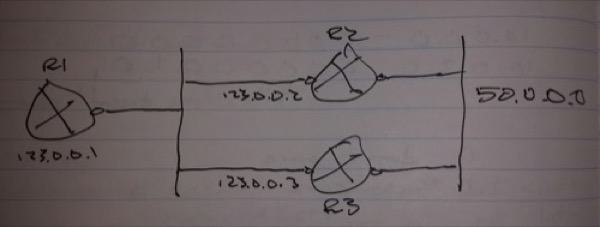
Scenario -> On R1, filter incoming update for network 50.0.0.0 if it is coming from R3
R1(config)# access-list 100 deny ip host 123.0.0.3 host 50.0.0.0
access-list 100 permit ip any any
router rip
distribute-list 100 in
Prefix Lists
– More flexible
– Can match on subnet masks
ip prefix-list <name> [seq <number] permit | deny <network/wildcard mask> [le | ge <0 – 32>]
– <network/wildcard mask> – prefix
– le | ge <0 – 32> – subnet mask
access-list <number> permit | deny <network> <wildcard mask>
10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
10.0.0.0 /22
10.0.0.0 /24
ip prefix-list LIST1 deny 10.0.0.0/8 ge 24 le 24
– Matches 10.0.0.0 /24
Match any network starting with 172.16.x.x with subnet mask from 255.255.0.0 to 255.255.255.0
255.255.0.0 -> /16
255.255.128.0 -> /17
255.255.192.0 -> /18
255.255.224.0 -> /19
255.255.240.0 -> /20
255.255.248.0 -> /21
255.255.252.0 -> /22
255.255.254.0 -> /23
255.255.255.0 -> /24
ip prefix-list ABC deny 172.16.0.0/16 ge 16 le 24
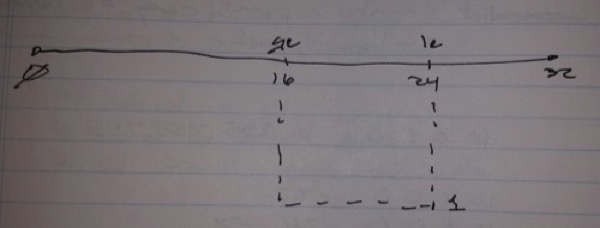
1.
– Wildcard ->16
– Range -> 16 – 24
2.
– Wildcard -> 16
– Range -> 18 – 32
-> If on the exam, upper boundary is not specific, assume it’s 32
3.
– Wildcard -> 16
– Range -> 18 – 24
ip prefix-list ABC deny 172.16.0.0/16 ge 18
ip prefix-list ABC deny 172.16.0.0/16 ge 18 le 24
Drawback of using prefix-lists
– ge cannot be lower than the wildcard mask
Scenario -> Match any network starting with 172.16.0.0 and subnet mask between 8 and 24
ip prefix-list ABC deny 172.16.0.0/16 ge 8 le 24
-> Will not work
-> ge cannot be lower than the wildcard mask
If a single subnet mask is to be matched and it happens to be equal to the wildcard mask, then ge and le can be skipped
– Compare first octet of 10.0.0.0 and subnet mask must be 255.0.0.0
ip prefix-list permit 10.0.0.0/8

Filter 1.1.1.1 /32 from R2
R1(config)# ip prefix-list ABC deny 1.1.1.1/32
ip prefix-list ABC permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
router rip
distribute-list prefix ABC out fa0/0
Filter from a specific source
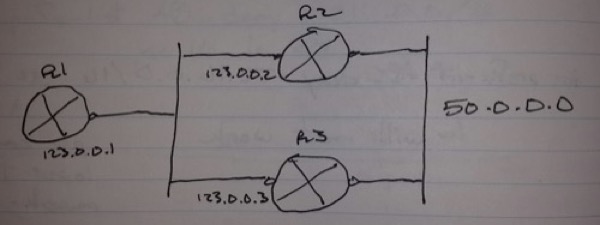
Scenario -> Filter any network coming from R3 and accept all networks from R2
– In this scenario, two prefix lists will be used
-> 1. To identify which networks will be filtered
-> 2. To identify the source
Distribute List
distribute-list prefix <list1> gateway <list2> in | out [<interface>]
R1(config)# ip prefix-list LIST1 permit 50.0.0.0/8
ip prefix-list LIST2 deny 123.0.0.3/32
ip prefix-list LIST2 permit 123.0.0.2/32
router rip
distribute-list prefix LIST1 gateway LIST2 in fa0/0
During the lab, always use extended ACLs unless using prefix-lists is spcified
sh ip protocols
– Displays the distribute-lists applied
Offset-list
– This is used to add an offset number to the metric value when updates are sent or received
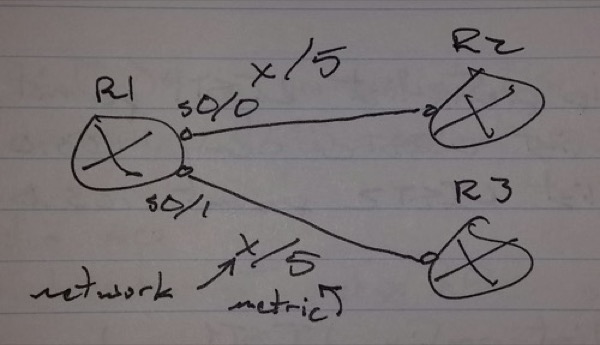
Scenario -> R1 should always use R2 as next-hop to reach network x (50.0.0.0)
– If connection to R2 goes down, R1 should start using R3 as next-hop for network x
offset-list <acl> in | out <offset-number> [<interface>]
– Standard ACL is used
access-list 1 permit 50.0.0.0
router rip
offset-list 1 in 2 s0/1
For filtering purposes, offset number 16 can be used
Scenario -> Filter all network from R3
access-list 1 permit any
router rip
offset 1 in 16 s0/1
– or –
! No ACL needed
router rip
offset-list 0 in 16 s0/1
Filtering By Manipulating AD
– AD 255
-> Unreachable
-> Route deleted from the routing table
Scenario -> Filter network 50.0.0.0 from any router
access-list 1 permit 50.0.0.0
router rip
distance 255 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 1
-> 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 – the source
-> 1 – ACL
Scenario -> Filter 50.0.0.0 from R3 (123.0.0.3)
access-list 1 permit 50.0.0.0
router rip
distance 255 123.0.0.3 0.0.0.0 1
RIP Miscellaneous Topics
– Change timers
– Unicast updates
– Triggered updates
– Send / receive version
Changing Timers
– rip configation
– inside interface
router rip
timers basic <update> <invalid> <holddown> <flush>
int fa0/0
ip rip advertise <sec>
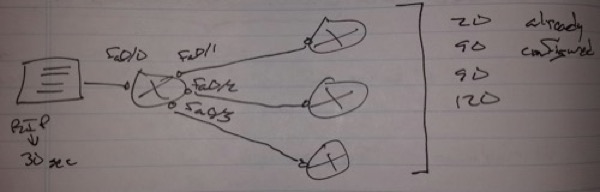
Scenario -> Change the RIP timers to 20, 90, 90, 120, but keep the update time to 30 seconds for fa0/0
R1(config)# router rip
timers basic 20 90 90 120
int fa0/0
ip rip advertise 30
Unicast Updates

To switch to unicast updates
– Stop sending multicast updates
– Start sending unicast updates
On R1 / R2:
router rip
passive-interface fa0/0
neighbor 12.0.0.x
Triggered Updates
– Any serial (point-to-point) interface the periodic updates can be disabled and made triggered
On R1 / R2:
int s0/0
ip rip triggered
debug ip rip
sh ip protocols
Send | Receive Version
– By default if the version command is not used, then all interfaces
-> Send v1 updates
-> Receive v1 and v2 updates
– If the version command is used, the interfaces will send and receive the version specified
– The impact of the version command can be overridden by using interface specific commands
int fa0/0
ip rip send version { 1 | 2 }
ip rip receive version { 1 | 2 }
sh ip protocols
router rip will not display in show run if a network statement is not configured
ip rip advertise 30 will not show up in the sh run config because it is the default configuration
– Use sh ip route to verify the proper networks are received on the interface

