IS-IS Notes
IS-IS:
– Link state routing protocol
-> 0xFEFE
-> 0x0800
– Connectionless Network Protocol (CLNP)
– Like an IP protocol suite in OSI model
-> Router
-> Intermediate System (IS)
-> End host
-> End System (ES)
-> OSI protocol
-> Direct
ly works over layer 2
-> Integrated IS-IS can have payload of IPv4 or IPv6
IS-IS uses the following parameters
– IS-IS Hello (IIH)
– Link State Packet (LSP)
-> Database IS-IS
– Complete Sequence Number PDU (CSNP)
-> A list of database entries
– Partial Sequence Number PDU (PSNP)
-> A request to send LSPs

Neighbor Formation
– IIH must match the following
-> Authentication
-> IS type
-> MTU
-> Priority
-> system-id / area-id
Link can be point-to-point or multi-access
– Network types
-> Point-to-point
-> Broadcast
-> DIS is elected (Designated Intermediate System)
-> Highest priority selected
-> Highest Subnet Point of Attachment (SNPA)
-> MAC address (ethernet)
-> Frame-relay DLCI
-> Highest system-id
-> DIS election is pre-emptive
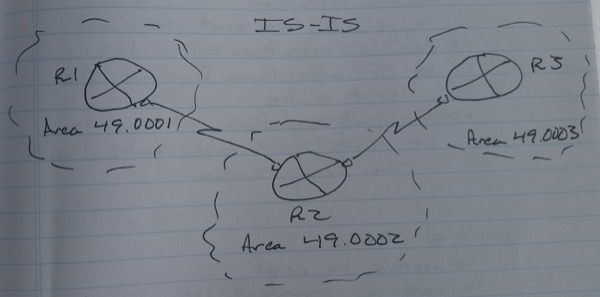
SNAP Address
– Subnetwork Access Point
– 20 butes represented in HEX
-> Bytes 1 – 13
-> area-id
-> Bytes 14 – 20
-> Network Selector Field
-> Always equal to “00”
A SNAP address with a NSEL part 0 Network Entity Title (NET) address
-> Must be an even number of bytes
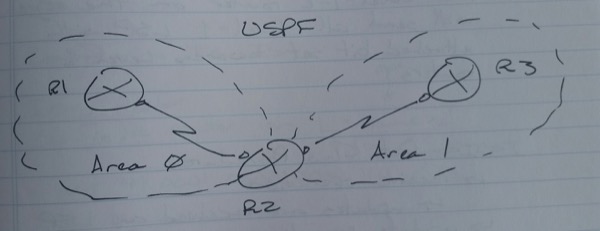
IS-IS Area and Backbone Network
– Level-1
-> Router configuration mode
-> Similar to a NSSA
– Level-2
-> Interface configuration mode
-> Similar to Area 0 routers
– Level-1-2
– The level decides which updates can be received
– Two routers can be in different areas and still form neighbors
-> This means IS-IS areas are per router, as opposed to OSPF which is area per-link
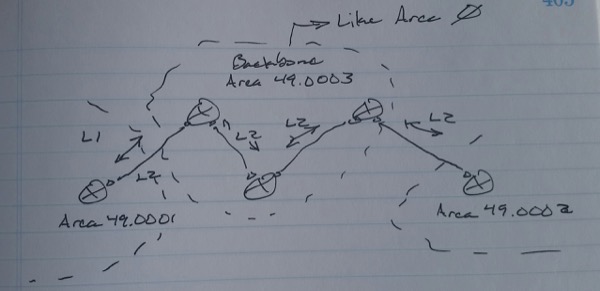
All routers and links, by default, are Level-1-2
– Within an area, L-1-2 neighbors can be formed
– Between areas, only L-2 neighbors can be formed
– A consecutive set of Level-2 adjacencies is called a backbone, which may include several routers
-> The Level-2 adjacencies cannot be discontiguous
– The Level-1-2 router on the edge will send all Level-1 LSP with attached it set towards Level-1 routers
IS-IS Data Flow Procedures
– Receive operation
-> Updates are received as LSP
– Update operation
-> Updates are sent as LSP
– Decision operation
-> SPF algorithm finding the best routes
– Forward operation
-> Create CEF table entries with the best routes
IS-IS Metric
– Metric is cost
– Cost is constant 10 everywhere
-> No calculation
– By default, “narrow metric” is used
-> 6 bit
-> 1 – 63
– Can be changed to “wide metric”
-> 2^24
– “Wide metric” is needed for MPLS TE
IS-IS Topology
– Single topology
-> IPv4 and IPv6 address-families share the same path calculation
-> IPv4 and IPv6 has to be enabled on all interfaces configured for IS-IS
-> The interfaces doesn’t necessarily need both IPv4 and / or IPv6 addresses configured
– Multi topology
-> IPv4 and IPv6 address-families calculate best paths independently
-> IPv4 and IPv6 configuration independent
-> Interfaces configured for IS-IS can have IPv4 enabled, IPv6 enabled, or both
– For IOS routers, the default configuration is single topology
– For XR routers, the default IPV6 configuration is multi topology
Configuring IS-IS
IOS Router
(config)# router isis [<name>}
-> default name is NULL
net 49.001.0000.0000.1111.00
int lo0
ip routing isis
ipv6 routing isis
int fa0/0
ip routing isis
ipv6 routing isis
XR Router
(config)# router isis <name>
net 49.0001.0000.0000.1111.00
-> area: area 49.0001
-> system: .0000.0000.1111
-> NSEL: .00
int lo0
address-family ipv4 unicast
address-family ipv6 unicast
int g0/0/0/0
address-family ipv4 unicast
address-family ipv6 unicast
show clns neighbor
show isis neighbor
-> “L1 L2 neighbors”
IOS (Level type, interface)
int e0/0
isis circuit-type level-1
XR (Level type, interface)
router isis ABC
int g0/0/0/0
circuit-type level-1
IOS (Level type, entire router)
router isis
is-type level-1
XR (Level type, entire router)
router isis ABC
is-type level-1
IOS (Timers)
int e0/0
isis hello-interval <sec>
isis hello-multiplier <count>
XR (Timers)
router isis ABC
int g0/0/0/0
hello-interval <sec>
hello-multiplier <count>
IOS
int e0/0
isis priority <value>
-> 0 – 127
-> 64 is default
isis metric <value> [ level-1 | level-2 ]
isis password <password>
isis network { point-to-point | broadcast }
Route Leaking
– Routes can be leaked from Level-1 to Level-2
– and visa versa
On IOS Level-1-2 Router
router isis
redistribute isis ip level-2 into level-1 { distribute-list <name> | route-map <name> }
access-list <number> permit | deny <protocol> <source> <wildcard> <destination> <wildcard>
-> network leaked – <source> <wildcard>
-> subnet mask to match – <destination> <wildcard>
Scenario -> Leak the loopback of R3 to R1
R2(config)# access-list 100 permit ip 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 0.0.0.0
ip prefix-list ABC permit 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
route-map LEAK
match ip add prefix-list ABC
XR
(config)# router-policy POLICY1
if destination in (3.3.3.3/32)
pass
end if
router isis ABC
address-family ipv4
propagate level-2 into level-1 route-policy POLICY1
IOS
(config)# mpls ip
mpls label protocol ldp
ip cef
int fa0/0
mpls ip
XR
(config)# mpls ldp
int fa0/0
int s0/0
root
commit
sh run mpls ldp
Potential Problems
Mismatched Level 1 and Level 2 interfaces
Misconfigured NSAPs (NET)
Duplicate system IDs
Mismatched MTUsx
Mismatched IP addresses and subnets
Mismatched topologies (single vs. multi)
Mismatched metrics (narrow vs. wide)
– Log Messages:
– TLV contents different, code 128
-> TLV 128 – IP Internal Reachability (narrow)
– TLV code mismatch
– TLV contents different, code 135
-> TLV 135 – Extended IP Reachability (wide)
Verification (IOS):
sh clns nei
sh clns is-nei
sh clns int
sh isis nei
sh isis spf-log
sh isis database
sh isis database detail
-> Use to determine whether single topology or multitopolgy is configured
sh isis ip topology
sh isis ipv6 topology
sh clns
sh clns protocol
-> Shows the metric types that are generated and accepted
sh ip protocols
sh ipv6 protocols
sh isis topology
sh clns nei detail
sh clns int <int>
sh ip route isis
sh ipv6 route isis
ping 2.2.0.8 source lo0
ping 2002:2:2::8 source lo0
debug isis adj-packets
debug isis update-packets
debug spf-events
Verification (XR):
sh isis
-> Shows the metric types that are generated and accepted
sh isis nei
sh isis int bri
sh isis spf-log
sh isis database
sh isis database detail
-> Use to determine whether single topology or multitopology is configured
-> Multitopology entries:
Metric: 10 MT (IPv6 Unicast) IPv6 2002:9:9::1/128
Metric: 10 MT (IPv6 Unicast) IPv6 2002:9:9:11::/64
Metric: 10 MT (IPv6 Unicast) IPv6 2002:9:9:18::/64
-> Singe topology entries:
Metric: 10 IPv6 2002:9:9::1/128
Metric: 10 IPv6 2002:9:9:11::/64
Metric: 10 IPv6 2002:9:9:18::/64
sh isis ipv4 topology
sh isis ipv6 topology
sh protocols
sh protocols ipv6
sh route isis
sh route ipv6 isis
ping 2.2.0.7 source 2.2.0.8
ping 2002:2:2::7 source 2002:2:2::8

